Your ears are a gateway to the world of sound, and maintaining their health is vital for your overall well-being. Beyond just hearing, your ears play a crucial role in balance, communication, and emotional connections. However, many people take ear health for granted until problems arise. Understanding how ear health influences overall hearing can help you adopt proactive habits to protect this essential sense.
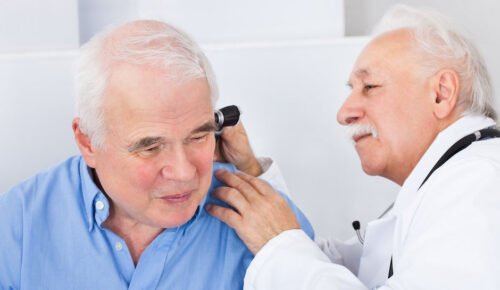
If you’re experiencing difficulties or suspect changes in your hearing, early intervention is key. Professional services like hearing tests Marrickville can identify issues early, enabling timely treatment and minimising long-term damage. In this guide, we’ll explore the connection between ear health and hearing, common issues, and how to preserve your auditory abilities.
The Anatomy of Hearing
To fully appreciate the importance of ear health, it’s essential to understand how hearing works. The ear comprises three main sections: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. Each part has a unique role in capturing and processing sound.
- Outer Ear
- Includes the ear canal and the visible part of the ear (pinna).
- Funnels sound waves toward the eardrum.
- Middle Ear
- Contains the eardrum and three tiny bones (ossicles).
- Amplifies sound vibrations and transmits them to the inner ear.
- Inner Ear
- Houses the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure filled with fluid and tiny hair cells.
- Converts vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve.
Damage to any part of the ear can disrupt this process, leading to hearing loss or other complications.
Common Ear Health Issues Affecting Hearing
Several conditions can impact ear health and hearing. Identifying these issues early allows for effective management and better outcomes.
- Ear Infections
Infections in the middle ear are common, especially in children. They can cause temporary hearing loss and, if untreated, may lead to more serious complications.
Symptoms:
- Ear pain.
- Fluid discharge.
- Difficulty hearing.
- Tinnitus
Tinnitus is characterised by a persistent ringing, buzzing, or humming sound in the ears. It can result from noise exposure, ear injuries, or underlying health conditions.
Impact:
- Interferes with concentration and sleep.
- May indicate hearing loss or ear damage.
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Exposure to loud sounds over time can damage the delicate hair cells in the cochlea, leading to permanent hearing loss.
Risk Factors:
- Loud music.
- Industrial noise.
- Prolonged headphone use at high volumes.
- Wax Build-Up
Excess earwax can block the ear canal, causing temporary hearing difficulties and discomfort.
Prevention:
- Avoid inserting objects like cotton buds into the ear.
- Use professional ear cleaning methods if necessary.
- Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis)
Hearing naturally declines with age due to wear and tear on the inner ear structures.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds.
- Trouble understanding speech in noisy environments.
The Connection Between Ear Health and Overall Hearing
Good ear health is integral to maintaining clear and effective hearing. Here’s how different aspects of ear health influence your auditory abilities:
- Clear Ear Canals for Sound Transmission
Blocked or inflamed ear canals disrupt the flow of sound waves to the eardrum. Regular cleaning and care prevent blockages that can impair hearing.
- Healthy Eardrum Function
The eardrum’s vibrations are crucial for transmitting sound. Damage from infections or physical trauma can reduce its efficiency.
- Preserving Inner Ear Hair Cells
Once damaged, the hair cells in the cochlea cannot regenerate. Protecting them from loud noises is vital for long-term hearing health.
- Effective Signal Transmission
Issues with the auditory nerve or brain’s processing centres can cause hearing loss, even if the ear structures are intact.
How Hearing Loss Impacts Daily Life
Hearing loss affects more than just the ability to perceive sound. It has far-reaching implications for physical, emotional, and social well-being.
- Communication Barriers
Hearing difficulties can make conversations challenging, leading to frustration and misunderstandings.
- Social Isolation
Struggling to hear in social settings may cause individuals to withdraw, leading to loneliness and reduced quality of life.
- Cognitive Decline
Studies have linked untreated hearing loss to an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
- Emotional Well-Being
Hearing loss can lead to feelings of anxiety, embarrassment, or depression, particularly when left unaddressed.
Tips for Maintaining Ear Health
Proactively caring for your ears can reduce the risk of hearing loss and other complications. Here are some practical tips:
- Protect Your Ears from Loud Noises
- Use earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones in noisy environments.
- Follow the 60/60 rule: Keep headphone volume below 60% and limit usage to 60 minutes at a time.
- Avoid Inserting Objects into Your Ears
- Refrain from using cotton buds or other sharp objects to clean your ears.
- Let earwax clear naturally or seek professional help if necessary.
- Maintain Hygiene and Health
- Keep your ears dry to prevent infections.
- Avoid smoking, as it can damage the tiny blood vessels in the ear.
- Monitor Your Hearing
- Pay attention to early signs of hearing loss, such as frequently asking others to repeat themselves.
- Schedule regular hearing tests, especially if you work in noisy environments or have a family history of hearing loss.
The Importance of Regular Hearing Tests
Hearing tests are essential for monitoring your auditory health and detecting issues early. A professional test evaluates your ability to hear different frequencies and levels of sound.
Benefits of Hearing Tests:
- Early Detection: Identifies problems before they worsen.
- Personalised Solutions: Helps professionals recommend treatments, such as hearing aids or lifestyle adjustments.
- Monitoring Changes: Tracks the progression of hearing loss over time.
Regular tests can be particularly beneficial for individuals exposed to loud environments or experiencing symptoms of hearing loss.
When to Seek Professional Help
While mild ear issues can often be managed at home, some situations require professional intervention.
Seek Help If You Experience:
- Persistent pain or discomfort in the ears.
- Sudden or significant hearing loss.
- Symptoms of an ear infection, such as fever or drainage.
- Persistent tinnitus or dizziness.
An audiologist, ENT specialist, or hearing clinic can provide a thorough assessment and recommend appropriate treatments.
Final Thoughts: Protecting Your Hearing for Life
Ear health plays a pivotal role in maintaining your ability to hear and enjoy the sounds of life. From understanding how your ears function to adopting preventative care practices, small steps can have a big impact on your auditory well-being. Regular monitoring, such as scheduling hearing tests, ensures you stay ahead of potential issues and address them early.
By protecting your ears from damage, maintaining good hygiene, and seeking professional help when needed, you can preserve your hearing and quality of life for years to come. Take charge of your ear health today—your future self will thank you.