In temperature-sensitive operations, consistency is more than just a buzzword—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re managing a pharmaceutical warehouse, a food production facility, or a data center, maintaining consistent temperature levels is critical to ensuring the quality, safety, and effectiveness of the products or processes within your operation. In this guide, we’ll explore the importance of consistency in temperature-sensitive environments, the challenges involved, and strategies to overcome them.
The Importance of Consistency in Temperature-Sensitive Operations
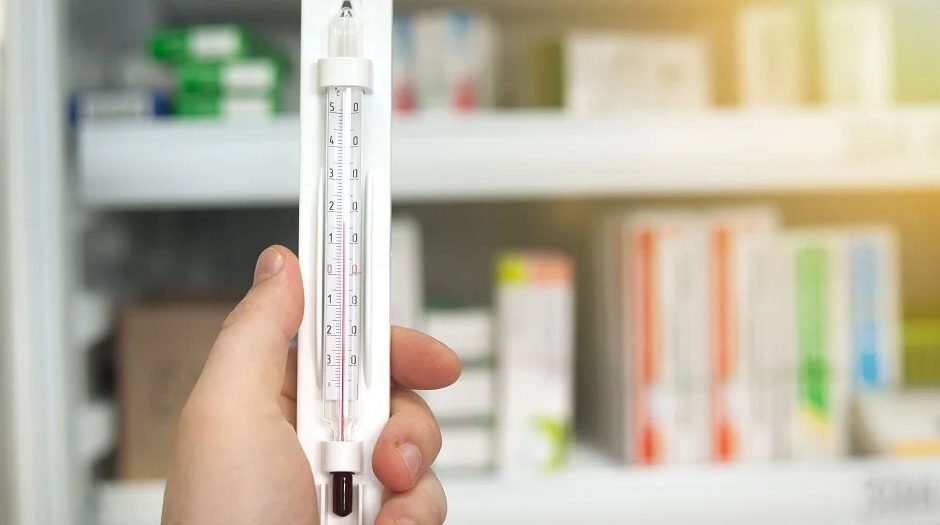
Temperature-sensitive operations are those in which even slight deviations from the optimal temperature range can lead to significant consequences. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, certain medications must be stored within a narrow temperature range to remain effective. Similarly, in food production, maintaining consistent temperatures is crucial to preventing spoilage and ensuring food safety.
A reliable temperature monitoring device is indispensable in these environments. This device provides continuous oversight of the temperature, ensuring that any fluctuations are immediately detected and addressed. It serves as the first line of defense against inconsistencies that could jeopardize the integrity of the products or processes.
Common Challenges in Maintaining Temperature Consistency
While the importance of temperature consistency is clear, maintaining it can be challenging. Several factors can contribute to temperature fluctuations, including equipment failure, human error, and environmental conditions. Understanding these challenges is the first step in developing effective strategies to overcome them.
Equipment Failure
Equipment failure is one of the most common causes of temperature inconsistencies. Refrigeration units, HVAC systems, and other temperature control devices are not immune to breakdowns, and when they fail, the temperature within the environment can quickly rise or fall outside of the safe range. Regular maintenance and the use of high-quality equipment are crucial to minimizing the risk of equipment-related temperature fluctuations.
Human Error
Human error can also lead to temperature inconsistencies. For example, leaving a freezer door open for too long or incorrectly setting a thermostat can cause the temperature to deviate from the desired range. While human error is difficult to eliminate entirely, training and the implementation of automated systems can help reduce its impact.
Environmental Conditions
External environmental conditions, such as extreme weather, can also affect temperature-sensitive operations. For instance, a heatwave can put additional strain on cooling systems, making it harder to maintain the desired temperature. In these cases, having robust systems in place, such as backup generators and insulated environments, can help maintain consistency.
Strategies for Maintaining Temperature Consistency
Given the challenges associated with maintaining temperature consistency, it’s important to implement a variety of strategies to ensure that your operation remains within the required temperature range. Here are some key approaches to consider:
Use of Advanced Monitoring Systems
One of the most effective ways to maintain temperature consistency is by using advanced monitoring systems. These systems continuously monitor the temperature in real-time, providing alerts if the temperature begins to drift outside of the acceptable range. By having immediate access to this information, you can take swift action to correct any issues before they become critical.
In addition to real-time monitoring, these systems often include features such as data logging and reporting, which can be invaluable for compliance purposes and for identifying patterns that may indicate underlying issues with your temperature control systems.
Automation and Redundancy
Automation plays a crucial role in maintaining temperature consistency, especially in operations where manual monitoring may not be feasible 24/7. Automated systems can adjust temperatures as needed without human intervention, reducing the risk of errors.
Redundancy is another key component of a robust temperature control strategy. This means having backup systems in place that can take over if the primary system fails. For example, having a secondary refrigeration unit or a backup power supply can prevent a minor issue from turning into a major problem.
Regular Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance of temperature control equipment is essential for preventing breakdowns that could lead to temperature inconsistencies. This includes not only routine checks and repairs but also the calibration of monitoring devices to ensure they are providing accurate readings.
A maintenance schedule should be established and strictly followed, with records kept of all maintenance activities. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they lead to significant temperature deviations.
Staff Training and Awareness
As mentioned earlier, human error can contribute to temperature inconsistencies. To mitigate this risk, it’s important to provide ongoing training for staff on the importance of temperature control and the correct procedures for maintaining it. This training should include how to use temperature monitoring devices, what to do in the event of a temperature deviation, and the potential consequences of failing to maintain the required temperature range.
In addition to training, fostering a culture of awareness around the importance of temperature consistency can help ensure that everyone in the operation understands their role in maintaining it.
Insulation and Environmental Controls
In temperature-sensitive operations, controlling the external environment is just as important as managing the internal one. Proper insulation of storage areas, using temperature-controlled packaging, and implementing environmental controls such as humidity regulation can all contribute to maintaining a consistent temperature.
These measures are particularly important in operations where external conditions can vary significantly, such as in transportation or storage facilities that are not climate-controlled.
Emergency Planning and Response
Despite your best efforts, there may be times when temperature consistency is compromised due to unforeseen circumstances, such as power outages or natural disasters. Having a well-defined emergency plan in place can help mitigate the impact of these events.
Your emergency plan should include procedures for quickly restoring temperature control, such as switching to backup systems or relocating temperature-sensitive items to a safer environment. It should also outline the steps to take if products are exposed to temperatures outside the safe range, including how to assess potential damage and whether the products can still be used.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Consistency
Technology is an invaluable ally in the quest for temperature consistency. From advanced monitoring devices to automated systems, technology can help you maintain the precise conditions required for your operation. However, it’s important to choose the right technology for your specific needs and to ensure that it is properly integrated into your overall temperature control strategy.
For example, in addition to using a temperature monitoring device, you might consider implementing IoT (Internet of Things) solutions that allow for remote monitoring and control of temperature-sensitive environments. This can provide additional peace of mind and enable more proactive management of temperature consistency.
Maintaining consistency in temperature-sensitive operations is essential to ensuring the quality, safety, and effectiveness of your products or processes. By understanding the challenges involved and implementing a comprehensive strategy that includes advanced monitoring systems, automation, regular maintenance, and staff training, you can overcome these challenges and maintain the necessary temperature consistency.
Remember, consistency is key—whether it’s in the temperature of your environment, the maintenance of your equipment, or the training of your staff. By prioritizing consistency, you can ensure the success of your temperature-sensitive operation and avoid the costly consequences of temperature fluctuations.