Derek Bryceson played a significant role in Tanzania’s journey towards independence and development. Born on December 30, 1922, Bryceson was a notable figure in the country’s politics and conservation landscape. He contributed to politics, conservation and social services in Tanzania, making him an influential personality in the region.
Early Life and Career of Derek Bryceson
Derek Bryceson was born in England but moved to Tanzania, where he became politically active. He was with the Royal Air Force in World War II and developed his resilience and leadership attributes. Bryceson returned to Tanzania after the war and became an ally of Tanzania’s first President, Julius Nyer Ere. His work for Tanzania’s independence movement landed him a seat in the new government.
Derek Bryceson’s Political Contributions
Bryceson was a social services and economic development politician. In 1957, he was Assistant Minister for Social Services and in 1959, Minister for Mines and Commerce. His policy work contributed to achieving social welfare and economic development of the emerging nation. Derek Bryceson served in these roles because he cared about Tanzanians and national unity.

Conservation Efforts
Bryceson left his most lasting legacy through conservation in Tanzania. As director of Tanzania’s national parks from 1964, he helped preserve the country’s biodiversity. His leadership helped found and protect several national parks to protect Tanzania’s natural heritage for future generations. In balancing development with environmental protection, Derek Bryceson showed a passion for conservation.
Personal Life and Legacy
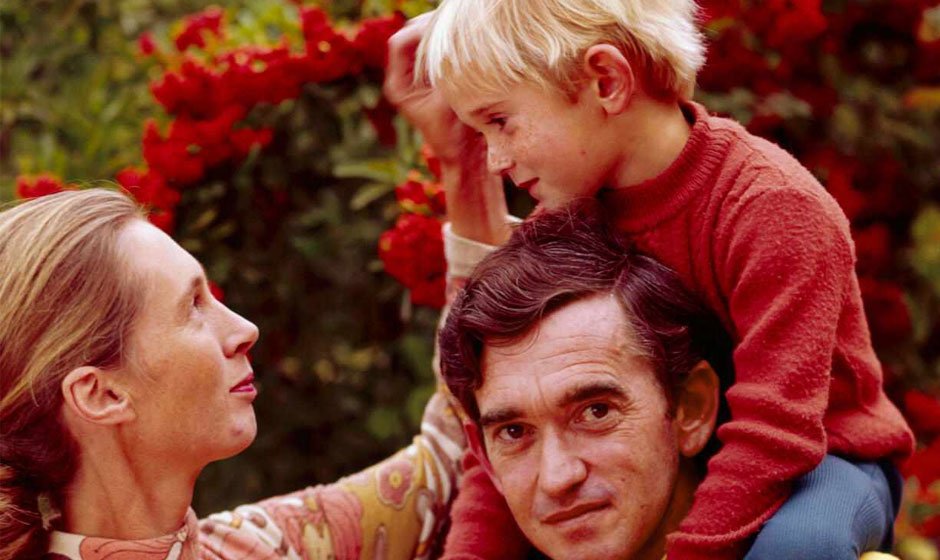
Derek Bryceson wed primatologist, Jane Goodall in 1975. Their marriage was one of respect and conservation passion. With the Tanzanian government job, Bryceson helped Goodall fund her research on chimpanzees and gave her the protection and money to continue her work. In 1980, Derek Bryceson died to cancer but left Tanzania a legacy of development and conservation.
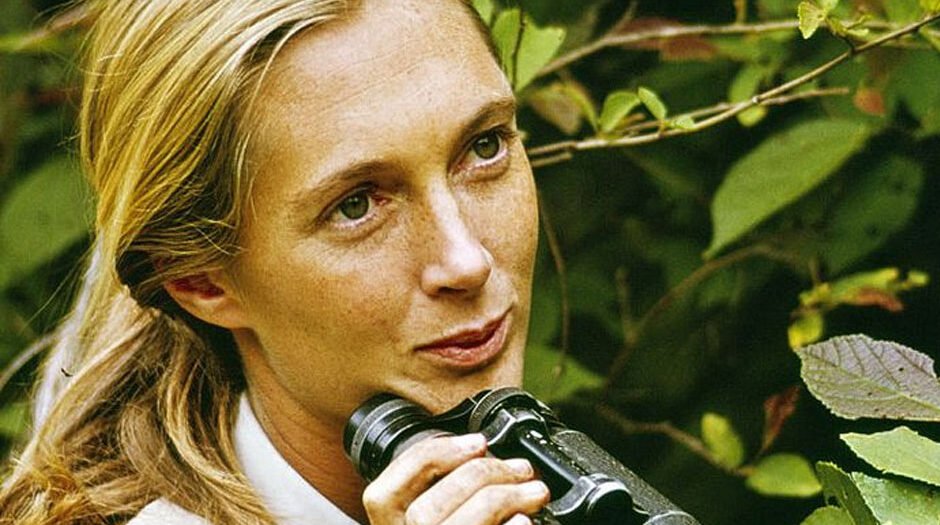
Who is Derek Bryceson’s Ex-wife – Jane Goodall?
Primatologist and conservationist Jane Goodall is best known for her work with chimpanzee population in Tanzania. Born April 3, 1934, in London, England, Goodall’s work has changed our perception of primates and their behaviour. She has become a wildlife conservation and animal welfare icon and environmental activist.
Jane Goodall’s Groundbreaking Research
In 1960, Goodall established a research camp in Gombe Stream National Park to study wild chimpanzees. Her observations challenged many accepted primate behaviours. She found chimpanzees make tools, hunt for meat and have complex social relationships. These findings revolutionized primatology.
Conservation and Advocacy
Beyond her studies, Goodall has been a champion for conservation and animal rights. In 1977, she established the Jane Goodall Institute for wildlife research, education and conservation worldwide. It also runs Roots & Shoots, a program that trains young people to work on environmental and humanitarian projects. Goodall has won numerous awards and honors – she was named a 2002 United Nations Messenger of Peace.
Conclusion
Derek Bryceson was an advocate for Tanzania development and conservation. His political work, social services and environmental protection have marked the nation. Bryceson shaped policies for economic growth and social welfare while preserving Tanzania’s natural heritage. His legacy inspires others to balance development with conservation – a commitment to people and environment.